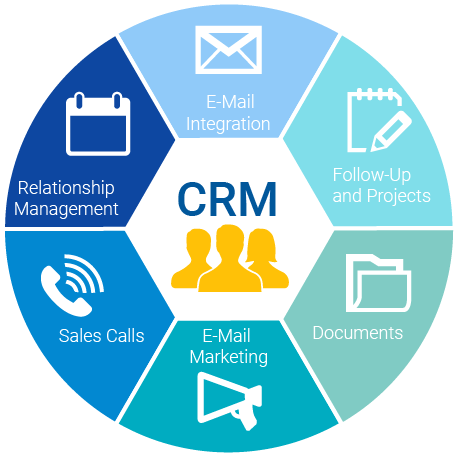
An ERP is an acronym for enterprise resource planning. It is basically a software or system that integrates functions, streamlines processes, and manages core business. An ERP can create value by integrated databases, collaboration, flexibility & mobility, and lowers costs. An ERP can also refer to a type of software that organizations use to manage day-to-day business activities such as accounting, procurement, project management, risk management and compliance, and supply chain operations. A legacy system is an old or out-dated system, technology or software application that continues to be used by an organization because it still performs the functions it was initially intended to do. They are also typically still used within a company because they tend to be reliable and familiar for their users. There are issues with legacy systems since they typically no longer have support and maintenance and they are limited in terms of growth. They also cannot easily be replaced. Since businesses evolve constantly due to changes in the economy, new laws, market conditions, management, reorganizations, etc., systems tend to become obsolete over time. Additionally, another system commonly used in companies is a CRM (customer relationship management). Sales, marketing, HR, strategy, and accounting typically use CRM’s. A CRM is a technology for managing all your company’s relationships and interactions with customers and potential customers. It can be a form of customer service. The goal or purpose of a CRM is to improve business relationships to grow your business. A CRM system helps companies stay connected to customers, streamline processes, and improve profitability. The main difference between a CRM and an ERP is that the ERP has an internal focus on the business, while a CRM has an external focus on its customers. They are both similar because they have shared data with a goal of increased profit. Additionally, two terms that relate heavily to data and CRM’s/ERP’s is velocity and veracity. Velocity refers to how quickly data is generated and how quickly that data moves. This is an important aspect for companies need that need their data to flow quickly, so it’s available at the right times to make the best business decisions possible. Veracity refers to the quality and accuracy of data. Gathered data could have missing pieces, may be inaccurate or may not be able to provide real, valuable insight. Veracity, overall, refers to the level of trust there is in the collected data. These terms relate to data integrity because it allows the company to have proof that the data is truthful and real, not made up. They also allow data scientists to derive more value from their data while also allowing the scientists’ organization to become more customer-centric. 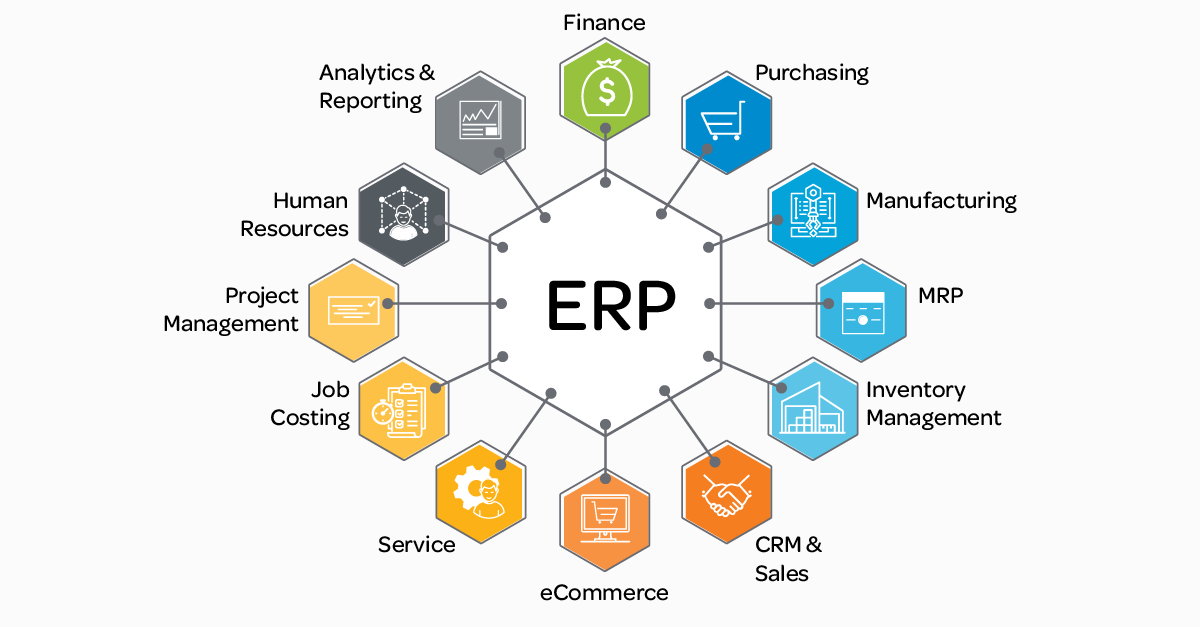
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.