Digital platforms are online businesses that facilitate commercial interactions between at least two different groups—with one
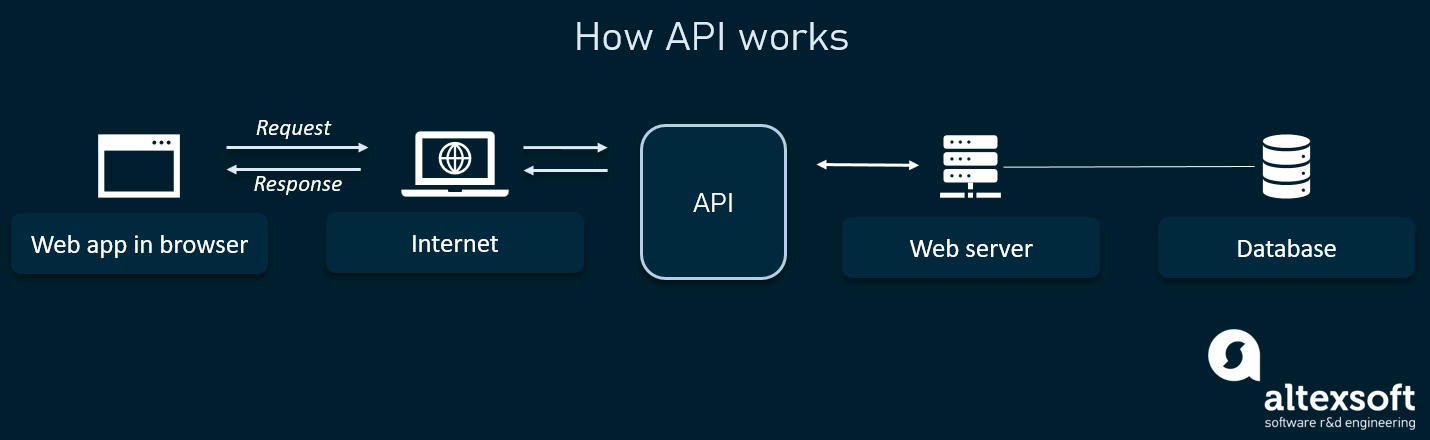
typically being suppliers and the other being consumers. They make it easier for companies to find customers, monetize assets, and reduce transaction costs. They are also beneficial for a company because they can reduce barriers to entry and making it easier for small suppliers to reach customers. By reducing the fixed costs needed to participate in the market, digital platforms also reduce prices and increase customer choice. The network effect, also known as the network externality or demand-side economies of scale, states that a good or service becomes more valuable when more people use it. Some examples of network effects can include e-commerce, such as eBay, Amazon, and Etsy. Another popular form of the network effect is social media platforms such as Instagram and Facebook. Additionally, Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet (“the cloud”) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. Some pros of cloud-computing can include: no administrative or management issues, easy accessibility, pay per use, and reliability. Additionally, some cons of cloud-computing can include: limited control of infrastructure, restricted/limited flexibility, ongoing costs, and security. There are three main different models of cloud services: software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PasS), and infrastructure as a service (IaaS). SaaS uses the internet to deliver applications, which are managed by a third-party vendor, to its users. SaaS is also commonly referred to as a cloud application service. An example of a SaaS could be Salesforce or Dropbox. PaaS provides cloud components to certain software while being used mainly for applications. On example of a PaaS could be Google App Engine. The last model of cloud-computing is IaaS, which is fully self-service for accessing and monitoring computers, networking, storage, and other services. It is made of highly scalable and automated compute resources. The main differences between these three models are that each model has a different specified features and functionalities. Each model is fit for anyone who is needing to switch to the cloud. An API (application programming interface) is basically a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a software interface, which means it offers a service to another piece(s) of software. API’s can build value based on what type of data they are actively consuming. Product managers are essentially the bind between the many functions that touch a product including design, customer success, sales, marketing, finance, legal, engineering, etc. They own the decisions about what gets built but also influence every aspect of how it gets built and launched. A typical product manager in todays world make trade-off decisions, and bring together cross-functional teams which ensure alignment between diverse functions.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.