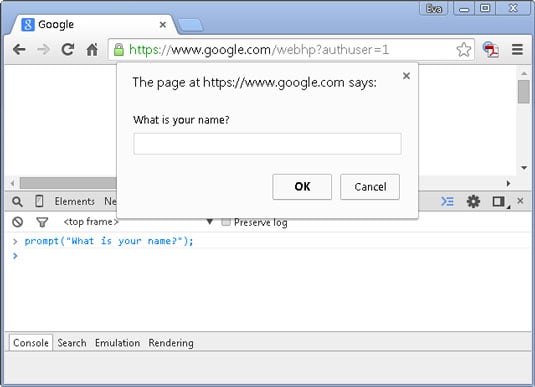
In JavaScript, a variable stores the data value that can be changed later on. To create a variable, use the “let” keyword followed by the name you want to give your variable. In JavaScript, you can either declare a variable or initialize one. The difference between these two terms is that when a variable is declared, the variable is registered using a given name within the corresponding scope (ex: inside a function). With initialization, when you declare a variable it is automatically initialized, which means memory is allocated for the variable by the JavaScript engine. There are a few rules / guidelines that come along when naming a variable in JavaScript which can include: your variable cannot start with a number, and spaces are not allowed. However, you can make your variables as long as you want and outside of the first character, your variable can include as many letters, numbers, and special characters as you want. The arithmetic operations in JavaScript include addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), division (/), and modulus (%). Addition adds two operands, subtraction subtracts the right operand with the left operand, multiplication multiplies two operands, division divides the right operand into the left operand with the result always being a floating-point number, and lastly, modulus divides the right operand into the left operand and returns the remainder. There are other arithmetic operations such as exponentiation, however the five arithmetic operations listed above are most commonly used in JavaScript. Concatenation is a very common task that allows you to combine separate strings together. Concatenation operators allow you to do this task and are coded as a + or +=. The + concatenation is used for concatenates two values, whereas the += adds the result of the expression to the end of the variable. The prompt () term lets you get input from the user. For example, you could use let myText = prompt(“Hello Earth”) to prompt the user with Hello Earth in a dialogue box.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.