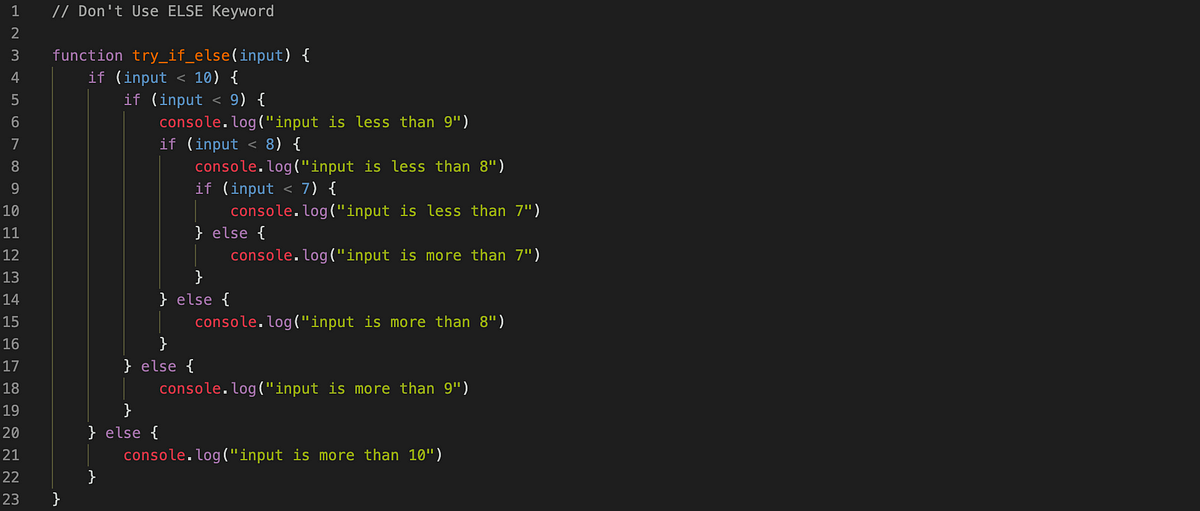
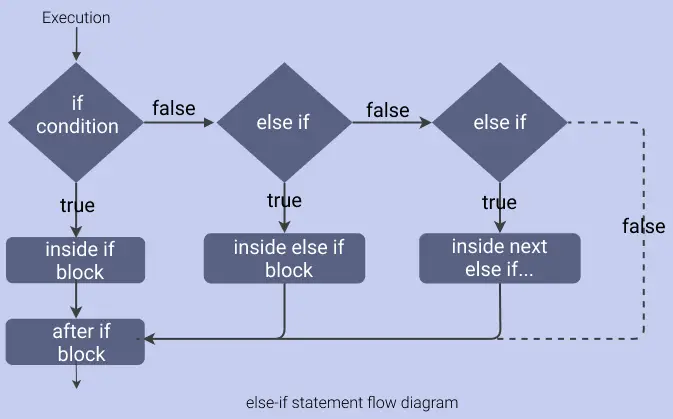
If and else statements allow you to run some code based on whether a condition is true or false. They can also be nested to help you stimulate more complex situations. The basic syntax of if/else if statements are if condition returns true then the statements inside the body of “if” are executed and the statements inside body of “else” are skipped. If condition returns false then the statements inside the body of “if” are skipped and the statements in “else” are executed. The purpose of isNaN is that the isNaN() method returns true if a value is NaN. The isNaN() method converts the value to a number before testing it. isNaN() is a global method. The term “global” means that it is available anywhere and everywhere in your JavaScript code. Some global methods are also called functions. We can evaluate && (an and function), if both the operands are true, for the result to be true. If any or both are false, then the result is false. The ||(or function), can be evaluated if one or both of the operants is true, then the result is true. An || function can only be false if both operants are false. Moving on, if statements are different than else-if and else statements because in an if statement, if the condition statement is true, then the condition statement executes and nothing more. This is different from else-if and else statements because if the condition is met in an else or els-if, then the statement executes, however if the condition is false, then a new statement or block up code is executed. An else statement does not take a Boolean Expression because an else statement is a negation of the corresponding if Boolean Expression.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.