Variables are used to store values (name = “Ivan”) or expressions (sum = x + y). Declare Variables in JavaScript Before using a variable, you first need to declare it. You have to use the keyword Let(var) to declare a variable like this: let name; You can assign a value to the variable either while declaring the variable or after declaring the variable. let name = “Ivan”;
The name must start with a letter (a to z or A to Z), underscore( _ ), or dollar( $ ) sign. After the first letter, we can use digits (0 to 9), for example, value1. JavaScript variables are case-sensitive, for example, x and X are different variables. Variable names should not begin with numbers. Initialization: giving an initial value to the variable. Declaration of a variable is informing the compiler with the variable name, the type of value the variable holds, and the initial value. In other words, there is only memory for a variable dispatched in the declaration. While in initialization there is a value set for that variable. Arithmetic operators are of 4 types Addition ?+?. Subtraction ?−?. Multiplication ?×?. Division ?÷?. The concatenation operator (+) concatenates two or more string values together and return another string which is the union of the two operand strings. The shorthand assignment operator += can also be used to concatenate strings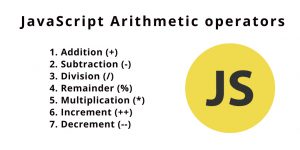
Hey Ivan,
These are great examples and resources you shared to get a better understanding of Javascript variables and string concatenation.An example helped me understand what a variable is and what it does.