An ERD is an Entity-Relationship Diagram. This diagram is a tool that can be used to identify the relationship between certain entities. These entities include things such as people, things, or concepts within a database. This diagram can prove to be useful for businesses as it helps to demonstrate the existing database, provides a visual aid for bug fixes, and provides a road map to design from as a new database or even update the old one. Within this diagram there are a few common symbols, they are:
Entities: represented by rectangles, and is an object or concept
Relationships: represented by diamonds, shows how two things share information
Attributes:represented by ovals, a characteristic of an entity (i.e. social security number, etc.)
Connecting Lines: solid lines connecting attributes and entities
Cardinality: the number attributed to the relationship. (i.e. one-to-one, many-to-one, etc.)
Furthermore, there are three types of ERD models.
Conceptual ERD: includes the entity and relationship
Logical ERD: includes the entity, relationship, and attribute
Physical ERD: includes the entity, relationship, attribute, attribute types and key.
The determination on which model is used is based on the businesses needs. If a business is looking for a high level view of a project, a conceptual ERD will likely be used. If a business is looking for a ground level view with technical details, a physical ERD would be the most useful choice.
Posts
6b: Loops
 Loops are handy when you want to run the same code repeatedly with different values in each execution. There are 3 types of loops in JS:
Loops are handy when you want to run the same code repeatedly with different values in each execution. There are 3 types of loops in JS:
for () loops → these loops contain 3 statements: the first is the initial expression, executed before the loop begins; the second is the condition that runs the loop; the third is the increment with each execution of the loop. If the second statement in a loop returns true, then the loop will begin again with the incremented value. If it runs false, the loop will end. A loop can also be ended using break, otherwise the loop will run forever if it can.
while () loops → these loops are used to repeat a block of code over and over until a certain condition (enclosed in the parentheses) is met. These are useful when you don’t know the exact amount of times you want the code to be repeated. The result of this expression will always be a Boolean value.
do…while () loops → this is a variation of the previous loop, except in this instance, the code is executed once before testing the condition. The loop will continue repeating as long as the condition is true.
Why is Salesforce important for us 1b
I believe Salesforce is extremely important to learn right now, and I think we are learning it because it is the next step of integrating technology into the workplace. Salesforce CRM has an incredible discovery, and is listed as one of the best/ most profitable places to work. A lot of my peers use Salesforce everyday at work. The benefits of creating a database on salesforce is that you are able to personalize it how it best suits you. There may be data that is more valuable than others, and with salesforce you are able to prioritize the information you are looking for.
The symbols of a swim lane consist of:
Circle: Indicates the beginning and end
Rectangle: an activity in progress
Diamond: decision that must be made
Arrow: Flow
Cylinder: Stored Data
Actors: are the people/departments that handle the different tasks
Process mapping is some form of graphic used to plan out a process step by step, showing the flow of completing a designated task. For the swim diagram provided I noticed the first problem 1.) Diagram does not start with a circle 2.) once it gets to Stock Manager, there is no option for if the product is out of stock 3.) For the deliver task it is represented with a cylinder that is supposed to represent stored data and 4.) the finish is also not represented with a circle! The ultimate benefit of a swim lane is the itemization of the steps in the process. It can help you have a better understanding of where potential problems may be, and you can have a birds eye view of the processes.
5b Post (Functions in Javascript)
A function in Javascript is a block of code that performs a specific task (programiz.com) You can create a function to do tasks such as adding, subtracting, etc. or color a draw a shape. Creating functions make your program easy to understand. When creating a function, you must use a syntax to declare that function. The function is declared using the keyword [function]. And when creating a name for the function, it should be descriptive. A function is written using { }. To use a function, you have to call it. When using a function return, you can return the value to a function call. Returning statement indicates that the function has ended. There are benefits of using functions. When you create a function, you can reuse it as needed. Functions makes your programs easier due to each task being broken down, and easier to read (programiz.com).
JavaScript function and function expressions. Programiz. (n.d.). Retrieved March 2, 2023, from https://www.programiz.com/javascript/function#:~:text=A%20function%20is%20declared%20using,the%20function%20add%20or%20addNumbers%20.
Understanding what MIS is all about 1a
After exploring the two different forms of the Software Development Life Cycle, I noticed some key differences between both waterfall and agile. For starters the waterfall model treats each phase as itemized events. Much like a natural waterfall, as you progress further and further, you cant go back up the waterfall! So as phase one completes and you proceed to the next, there is no backtracking, this helps improve the overall flow of the process. As for the agile model, the developers that have adopted this method understand that in this field specifically things can go of course easily. So because of this, the agile method has individual phases running at the same time, rather than following a step by step procedure. I think MIS is a way to gather, record, and distribute information in an efficient manner. Having used CRMs/ Apps/ etc. It is easy to see that they all revolve around DATA, and that is where MIS steps in to help organize that data.
For my normal day, a few parts of that system would include morning hygiene (i.e shower, brushing teeth, deodorant), travel (getting gas/driving/ cleaning windshield), Preparation for work ( prepare the calls/ schedule) and then I would say health (eating/ exercise), and then sleep!
The four core processes of designing UX (user experience) include user research, design, testing, and implementation. During the readings we came across some important acronyms which includes SDLC ( Software Development Life Cycle) like we talked about earlier explaining the difference between waterfall and agile. As for API ( Application Programming Interface) we spoke about this in class, and it was explained to me that Google maps was an example of an API because companies like Uber obviously did not map the world but they were able to use googles API for this app! UX simple enough stands for (User Experience) which seems to be the main focus of systems is to provide quality content. Finally we review ERP (Enterprise resource planning), which refers to another type of software that helps with organization and planning. A system is group of things working together towards a common goal, and there are three main components that play a role In that. Often referred to as IPO (Input, Process, Output) these three things all contribute to a system.
System analysis basically looks to achieve optimal production for either a procedure or business. Some times perceived as being a “problem-solving technique” Where you itemize all the different components of a system and see if each piece works well with each other! System analysis is an extremely broad term, as we have learned a “system” can refer a few things, so analyses can differ depending on the procedure or business. Im not too sure what the core of all systems is. If I had to give you my best answer it would be Data.
I believe MIS professionals are able to implement the right strategies to help improve overall production and efficiency. These people are constantly reviewing data, constructing it in an easy-to-understand way for businesses. MIS professionals are the best at taking data and making it easier to manage
6a: Conditional Statements in JS
Conditional statements are used in JavaScript to perform distinct actions based on a set of conditions and determines whether a code can run. If the condition is true the code can run, and if it is false it cannot run. if / else is the most common conditional statement in JS. A condition is enclosed in the parentheses after the if statement, and the resulting output is enclosed in curly brackets. The code tests to see if the condition is true. If there are multiple conditions, they can be declared using else if (different condition). The output will run for the condition that tests true. If all conditions test false, then the output for else {} will run.
example:
if (condition) {
var output = “output”;
} else if (different condition) {
var output = “output2”;
} else if (different condition) {
var output = “output3”;
} else {
var output = “output4”;
}
5b: Functions in JS
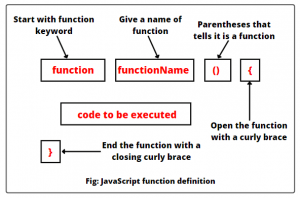
In JS, a function is a reusable block of code designed to perform a specific task to avoid having to reenter the same information over and over, creating a cleaner code and saving a lot of time. They can be executed as many times as needed.
They are defined by the word ‘function’, followed by whatever you wish to name the function, a set of parentheses (that contain the arguments for the function, however arguments are not necessary for the function to run), and then curly brackets that enclose the code to be executed. Once defined, a function can be used by entering the name and parentheses. The parentheses can be left blank if there are no arguments, but must contain a value if there are. Multiple arguments are separated by commas inside the parentheses.
5a: JavaScript Variables
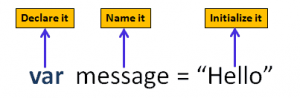 A variable in JavaScript is a way to name the storage of a piece of data, so that the data can be referred to throughout the code by its variable name as opposed to reentering the data every time. Declaring a variable is indicated by var or let followed by what you wish to name the data, and to assign a value you would add an equals sign followed by the value. If you want to return a string, the value must be in single or double quotation marks (ex: let myText = “Today is March 2nd”.) There are rules as to what a variable can be named in JS: it can only start with a letter, an underscore, or a $. Though they can’t start with a number, a variable name can have numbers in it after the first character. It’s important to remember that JavaScript is case-sensitive, so myVariable1 & MyVariable1 would represent different pieces of data.
A variable in JavaScript is a way to name the storage of a piece of data, so that the data can be referred to throughout the code by its variable name as opposed to reentering the data every time. Declaring a variable is indicated by var or let followed by what you wish to name the data, and to assign a value you would add an equals sign followed by the value. If you want to return a string, the value must be in single or double quotation marks (ex: let myText = “Today is March 2nd”.) There are rules as to what a variable can be named in JS: it can only start with a letter, an underscore, or a $. Though they can’t start with a number, a variable name can have numbers in it after the first character. It’s important to remember that JavaScript is case-sensitive, so myVariable1 & MyVariable1 would represent different pieces of data.
There are a few ways to display outputs:
console.log() to test code on the console
alert() to create a popup
document.write() to write directly on the webpage
Concatenation is putting two strings together and can be done with a + or += :
Example with + →
firstName = “Steven”, lastName = “Sclarow”
fullName = lastName + “,” + firstName
fullName= “Sclarow, Steven”
Example with += →
let a = 10;
let b = “hello”;
console.log( a += 5 ); // this is addition
// Expected output: 15
console.log( b += “world” ); // this is concatenation
// Expected output: “hello world”
4b: Cybersecurity
 Accompanying the digital revolution is our reliance on digital systems, as well as the risk that comes with it. Technology will continue to grow exponentially, and threats evolve with an ever changing digital landscape. Hackers are able to move fast, and as soon as a hole in a system is patched up they’re already finding another way in. Businesses and institutions realize the growing risk of cyberattacks and certain sectors, like finance, invest a lot of money into cybersecurity and are subsequently not considered the largest targets (in terms of the number of attacks, when they are attacked, they face huge financial consequences.)
Accompanying the digital revolution is our reliance on digital systems, as well as the risk that comes with it. Technology will continue to grow exponentially, and threats evolve with an ever changing digital landscape. Hackers are able to move fast, and as soon as a hole in a system is patched up they’re already finding another way in. Businesses and institutions realize the growing risk of cyberattacks and certain sectors, like finance, invest a lot of money into cybersecurity and are subsequently not considered the largest targets (in terms of the number of attacks, when they are attacked, they face huge financial consequences.)
While in class we discussed healthcare being a major target of ransomware attacks because of its overall reliance on legacy systems, another target that made up a larger % of attacks in 2022 was the educational sector. Most institutions, however, don’t pay the ransom, and in fact only 3 out of the 45 reported cyberattacks paid the hackers off. Despite this, the educational sector has seen the amount of attacks double from 2021 to 2022. This is because schools are easy targets with a lot of personal information on their students, parents, faculty, etc… Lack of funding means many schools nationwide don’t spend a significant amount on cybersecurity, and the systems in place are vulnerable and often outdated. Additionally, public schools within a designated locale operate on the same networks, servers, systems, etc, meaning that if a hacker can get into one school’s database, it’s easy to gain access to multiple schools.
Schools have become the leading targets of ransomware attacks – CBS News
4a: SaaS vs PaaS vs Iaas
When should you purchase software, platform, or infrastructure services?
Software-as-a-Service: allows companies to manage their data without the tediousness of having to develop their own software. SaaS uses a subscription-based web delivery model and vendors handle the technical side of things, streamlining processes for businesses. This option is best for small companies who don’t have the time or resources to develop their own, short-term projects, applications that aren’t used often, and apps that need both web & mobile access. Examples: Dropbox, Salesforce, Google Workspace
Platform-as-a-Service: this provides developers a framework for creating customized applications. This allows the devs to focus on the launching of applications while servers are managed by vendors. PaaS is also delivered via web and allows users to create software on their platform. This option is more scalable than SaaS and makes it easier for devs to manage by greatly reducing the amount of code needed without having to worry about maintaining the software. PaaS is useful when multiple devs are working on the same project, for creating customized applications, and for rapid deployment of applications. Examples: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, Windows Azure
Infrastructure-as-a-Service: IaaS is a completely self service cloud computing model that gives entities full control over their application management, middleware, data storage, etc, while the vendors are responsible for managing servers and networking. This model is the most scalable of the three and is typically delivered via API or dashboard. Additional resources are available to purchase as needed, cost varies depending on consumption. This option is good for large companies, companies experiencing rapid growth, or startups who want to avoid spending resources on purchasing hardware and software. Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine