Yiran Su
Week 14 Angst et al _Yiran
Social contagion theory suggests that when performance is uncertainty, decision makers will imitate others within their ecosystem. Such contagion occurs either through the direct transmission of information during interactions between adopters and nonadopters, or via an observational process where managers scrutinize their environment and attend to the adoption decisions of other organizations. Based on social contagion theory, the author hypothesized a hospital’s likelihood of adopting EMRs as a function of its susceptibility to the influence of prior adopters, its proximity to prior adopters, and the infectiousness or potency of influence exerted by adopting hospitals.
They apply a heterogeneous diffusion model (HBM) technique to perform a temporal analysis of the dynamic contagion process, using archival data from a sample drawn from an annual survey spanning 1975 to 2005 of almost 4,000 U.S. hospitals. 7 out of 9 hypotheses are supported, suggesting that with respect to susceptibility to influence, greater hospital size and age are positively related to the likelihood of adoption for nonadopters. Also, the adoption of EMRs by young and large or old and small hospitals exerts almost no infectious influence on potential adopters, whereas adoption by large, old hospitals is the most contagious. A hospital’s “celebrity” status also contributes to its infectiousness. Furthermore, they also find strong effects for social proximity on a hospital’s likelihood of adoption, and regional effects for spatial proximity. In contrast to a view that size and age are impediments in innovation because they create apathy in organizations, maturity provides more opportunities for learning from others. This study yields important insights into what factors increase the likelihood of adoption of EMRs, which will benefit both practitioners and researchers.
Week 12 Slage et al. 2015 Yiran
Understanding the triggers of senior managers’ IS investment decisions is important for both IS scholarship and IS practice. In this paper, the authors integrate insights from the behavioral theory of the firm and neoinstitutional theory to better understand how hospital senior managers make decisions about how and how much to invest in IS. Building on the understanding of IS investments as a form of organizational search, they argue that at least four recurring search mechanisms (i.e. problemitics search, institutionalized search, mimetic search and slack search) will influence the decision of the amount of resources allocated to IS.
Problemistic search is defined as search that is stimulated by a problem and is directed toward finding a solution to that problem. Slack search refers to a process that when resources are viewed as being in surplus, senior managers will seek to identify promising investment opportunities. Institutionalized search is commonly known as search conducted by organizations, which tends to be orderly, standardized, and somewhat independent of success or failure. Mimetic search can be conceived as a “search for information about what organizational characteristics are legitimated in their environmental niche. The first two search mechanism can be explained as behavioral search mechanism, while the last two are supported by neoinstitutional theory.
They draw on panel data from all 153 nonspecialist public hospital organizations in England. Findings from our dynamic panel data analyses suggest that hospital managers’ IS investment decisions are driven not only by the desire to improve organizational performance (problemistic search), but also by the need to achieve continuity in resource allocation (institutionalized search) and to signal compliance with external norms and expectations (mimetic search). The objective of making adequate use of uncommitted resources (slack search), however, was found to be salient as a trigger of IS investments only among hospital organizations with low regulative legitimacy.
Week 11_Aral et al 2012 Yiran
The authors propose that some information technologies could complement such incentive practices. They develop an analytical model that illustrates this complementarity and demonstrate how the corpresence of IT and incentive practices can explain variation in both the returns to IT and the effectiveness of performance pay contracts and human resource (HR) analytics practices that monitor and provide feedback on performance. A principal–agent model is used with moral hazard to illustrate the complementarity of HCM software and compensation systems that include HR analytics practices and performance pay.
To test three-way complementarities between performance pay, HR analytics, and IT, they used a data set surveying the detailed human resource practices of these 189 firms in 2005, of which about half (90) adopted the HCM system. To distinguish the reverse causality, that is, firms may choose to adopt HCM when they perform well or experience exogenous shocks to productivity. The authors separately measure the decision to invest and the actual investment itself.
The results show that the adoption of HCM software is greatest in firms that have also adopted performance pay and HR analytics practices. Furthermore, HCM adoption is associated with a large productivity premium when it is implemented as a system of organizational incentives, but has less benefit when adopted in isolation. The system of three-way complements produces disproportionately greater benefits than pairwise interactions, highlighting the importance of including all three complements.
Week 10_Proposal
Political and IT
The authors theorize that the national politics significantly affects IT investments in the federal government we discuss how the U.S. Congress influences federal IT investments. They hypothesize that a federal agency’s capacity-building IT investments are associated with (i) legislative approval for the chief executive, (ii) government dividedness, and (iii) the agency’s ideological characteristic. They adopt a panel dataset from 135 federal agencies and bureaus in 2003-2016, the empirical analyses support all the hypotheses. It is demonstrated that the national politics has a significant impact on their IT investment profiles. A federal agency is more likely to make capacity-building IT investments when its chief executive is blessed with legislative approval, when the federal government is more united, and when it is ideologically more moderate They suggest in order to make more capacity-building IT investments, a federal agency needs more policy directives, greater political support and legitimacy, and sufficient resource endowment from Congress.
However, they did not analysis the effectiveness of IT investment or any other outcome variables of IT investment in the study.
we discuss how the U.S. Congress influences federal IT investments. They hypothesize that a federal agency’s capacity-building IT investments are associated with (i) legislative approval for the chief executive, (ii) government dividedness, and (iii) the agency’s ideological characteristic. They a panel dataset from 135 federal agencies and bureaus in 2003-2016, the empirical analyses support all the hypotheses. It is demonstrated that the national politics has a significant impact on their IT investment profiles. A federal agency is more likely to make capacity-building IT investments when its chief executive is blessed with legislative approval, when the federal government is more united, and when it is ideologically more moderate They suggest in order to make more capacity-building IT investments, a federal agency needs more policy directives, greater political support and legitimacy, and sufficient resource endowment from Congress.
Week 8 How to write a lot
Week 8 Book recommendation How to write a lot
- Set milestone. For example, I will write one page on Monday. I need to finish 10 pages by this week
- Writing is a accumulating process. You don’t get a good paper in one iteration. I write a lot in the beginning without thinking the quality of English. I will improve it after I read it several time or re-write.
Week8_Mani et al. Yiran
Captive centers are wholly-owned by the multinational corporations (MNCs) to conduct the R&D and new product development offshore, which also refers to captive offshoring. Previous research indicates that the performance of distributed work is adversely impacted by failures of cooperation, i.e., misaligned incentives, as well as failures of coordination. The authors analyzed survey data from 132 R&D CCs established by foreign multinational companies in India to understand how firms execute distributed innovative work.
There are two generic categories of coordinating mechanisms for building and maintaining common ground, namely, information sharing and modularization. The information sharing strategy involves ongoing communication between interdependent agents to dynamically update common ground. A modularization strategy involves limited ongoing interaction between the agents. The author aim to examine the moderation role of three task attribution: task routineness; task analyzability and task familiarity. The hypothesis are listed below:
Hypothesis 1A (H1A). With high interdependence,
higher levels of modularization will increase performance
only when task routineness is high; when task routineness is low, higher levels of modularization will decrease
performance.
Hypothesis 1B (H1B). With high interdependence,
higher levels of modularization will increase performance
only when task analyzability is high; when analyzability is low, higher levels of modularization will decrease
performance.
Hypothesis 1C (H1C). With high interdependence,
higher levels of modularization will increase performance
only when task familiarity is high; when task familiarity is low, higher levels of modularization will decrease
performance.
Hypothesis 2A (H2A). With high interdependence,
information sharing as a coordination mechanism will
increase performance only when routineness is low; when
routineness is high, higher levels of information sharing
will decrease performance.
Hypothesis 2B (H2B). With high interdependence,
information sharing as a coordination mechanism will
increase performance only when analyzability is low; when
analyzability is high, higher levels of information sharing
will decrease performance.
Hypothesis 2C (H2C). With high interdependence,
information sharing as a coordination mechanism will
increase performance only when task familiarity is low;
when task familiarity is high, higher levels of information
sharing will decrease performance.
Regarding the first set of Hypothesis. Hypothesis 1A and 1b are supported, showing that Modularization improves performance only when routineness and analyzability are high. In terms of the second set of hypothesis, results are consistent with the interaction plots, which show that on average, information sharing improves performance for R&D work. However, a significant difference in slopes between high and low levels of task attributes is observed only in comparing projects of low versus high familiarity. The difference in slopes for the other
task variables is insignificant. Only Hypothesis 2C is supported.
The key contribution of this study lies in the careful explication of the conditions under which choice of investments in modularization versus information sharing yield different performance outcomes.It shows that the success of this strategy has to be evaluated based on the nature of the underlying work.
Gopal and Koka 2012_ Yiran
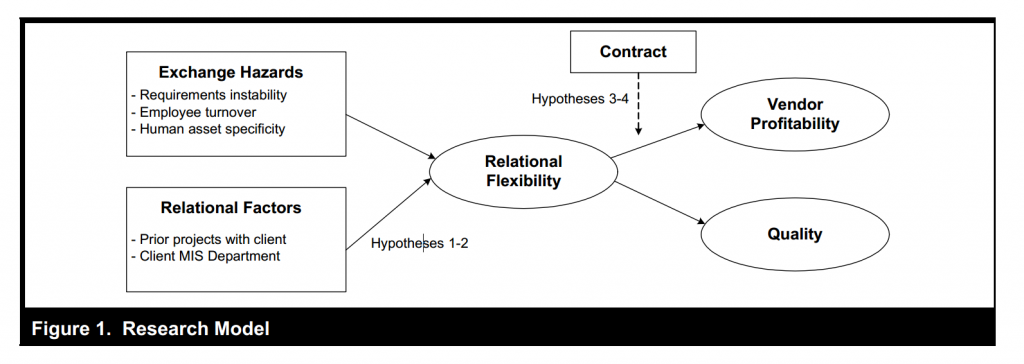
The authors examine the interacting effect of formal contracts and relational governance on vendor profitability and quality in the software outsourcing industry. They focus on the presence of relations flexibility in the exchange relationship, a critical manifestation of relational governance. They hypothesize that 1.relational flexibility provides greater benefits to an exchange partner that faces the greater proportion of risk in a project, induced through the contract; 2. The benefits manifest on the performance dimensions that are of importance to the risk-exposed partner.
The proposed the following model to test their hypothesis. They proposed two sub model: the relational flexibility model and the profitability and quality model. To operationalize the focal variable relational flexibility, they measure it as an observed outcome that represents ex post, extra-contractual aspect of the relationship. They identify five areas, namely payment procedures, warranty and liability conditions, installation and testing procedures, disputes resolution and project management. In terms of the dependent variables, the project profit was measured using the data collected from the company data base for each project. The service quality is measured by a five-item survey.
The author used muli-pronged analytic strategy to test the hypotheses. To solve the problem of the endogenous interacting variables, besides the OLS and 3SLS, they also use the Treatment effect model. All the hypotheses are supported, showing evidence for the argument that asymmetric benefits from relational flexibility to different contracting parties in an outsourcing relationship. The results also indicates that relational flexibility positively affects profitability in only fixed price contracts, where the vendor faces greater risk, while positively affecting quality only in time and materials contracts, where the client is at greater risk.
Agent Theory_Yiran
‘Agency Theory’
A supposition that explains the relationship between principals and agents in business. Agency theory is concerned with resolving problems that can exist in agency relationships; that is, between principals (such as shareholders) and agents of the principals (for example, company executives).
Week 6 Kirsch et al. (2002)_Yiran
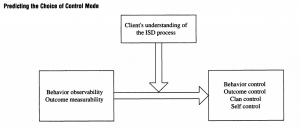
Firms have begun to utilize a client liaison role as a means of fostering business unit ownership and leadership of IS projects, which exercise control of IS project leaders to ensure that IS projects make progress in conformance with the business value propositions and proposed schedules and budgets. This paper aims to examine the exercise of project control across the client-Is relationships that may take on a variety of forms (hierarchical and lateral settings). The author defined control as all attempts to motivate individuals to achieve desired objectives, and it can be exercised via formal and informal modes.
The research model suggests that the client liaison’s choice of control mode is dependent on behavior observability and outcome measurability. This relationship between antecedent conditions and control modes is moderated by the client liaison’s understanding of the information. Based this mode, four hypotheses are developed
HYPOTHESIS1. High levels of outcome measurability will be associated with the exercise of outcome control. (Supported)
HYPOTHESIS2. High levels of behavior observability and client’s understanding of the IS development process will be associated with the exercise of behavior control. (No interaction, but main effect)
HYPOTHESIS3. High levels of behavior observability and low levels of client understanding of the IS development process will be associated with the exercise of clan control. (Supported)
HYPOTHESIS 4A. Low levels of outcome measurability will be associated with the exercise of self-control. (Partial supported)
Data were gathered from a questionnaire survey of 69 pairs of clients and IS project leaders. Regression analysis was used for hypothesis testing. The results of this study provide support for most of the hypothesized antecedents of the exercise of control by client liaisons. The distinctive finding of this study is that high behavior observability is associated with the use of either behavior or clan control. However, the key limitation is the moderate sample size.
Week 5_Grewal et al.(2006)_Yiran
This paper examined the effects of network embeddedness—or the nature of the relationship among projects and developers—on the success of open source projects. The key of understanding this paper lies in knowing how authors operationalize the key concepts, social capital and network embeddedness. They view social capital as the relations among developers, including project managers, and projects that provide developers access to information and (perhaps) embedded resources. In this paper, they refer the effect of social capital as network embeddedness. The term “network embeddedness” was used to to capture the architecture of network ties, and then three sub-constructs are defined to represent network embeddedness, i.e., structural, junctional, and positional embeddedness. Specifically, they used degree centrality—the number of projects in which the manager participates—to operationalize structural embeddedness, betweenness centrality—the number of paths between other nodes on which the manager lies—to operationalize junctional embeddedness, and eigenvector centrality—the manager participates in important projects—to operationalize positional embeddedness.
The author argued that high-quality information should be more useful in newer projects, and the value of project manager embeddedness should decline as projects age. In this case, Technical success was measured as the number of concurrent versioning system (CVS) commits. With respect to commercial success of the project, since project network embeddedness would facilitate the dissemination of this information. they assumed that the valence of the salient reputation dimension is positive (negative), word of mouth should increase (decrease) the commercial success of the project. Thus, project network embeddedness can have a positive or a negative effect on commercial project success. Commercial success was measured by the number of downloads over the life of a project.
Latent class regression analysis was used to show that multiple regimes exist and that some of the effects of network embeddedness are positive under some regimes and negative under others. The result confirmed that considerable heterogeneity exists in the network embeddedness of open source projects and project managers. Overall, the results for the effects of embeddedness are much stronger for technical success than for commercial success, implying that network embeddedness has a greater role to play in technical success than in commercial success.
Theoretically, this paper recognized that the effect of network embeddedness varies with the dependent variable, i.e., technical or commercial project success. Managerially, the results showed that projects with more developers see greater technical success in the later stages of project development, i.e., as the projects age.
Ceccagnoli 2012—Yiran Week 4
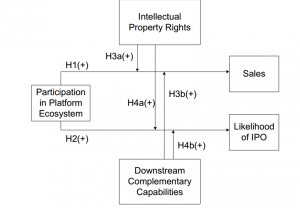
This paper investigated whether participation in an ecosystem partnership will improve the business performance in the context of the enterprise software industry (ISV). The key research questions of this study are (1) Is participation in a platform ecosystem, on average, associated with an increase in performance? (2) How is this improvement in performance affected by an ISV’s ownership of IPRs and specialized downstream capabilities? Two critical performance measures for ISVs were used as DV in this paper: sales and the likelihood of obtaining an initial public offering (IPO). They used a longitudinal data set of 1,210 small ISVs over the period of 1996 – 2004, with information on both ISVs’ decisions to join SAP’s platform ecosystem and information on their business performance. To operatize the participation in platform ecosystem (IV), they also collect partnership formation events through press releases. The stock of software trademarks registered in the United States is used as the measurement of another IV. The research framework is shown in Figure 1
Except for H4b, all the hypotheses are supported, showing that ISVs can achieve significant benefits through participation in a platform ecosystem. Joining a major platform owner’s platform ecosystem is associated with an increase in sales and a greater likelihood of issuing an initial public offering (IPO). Furthermore, these impacts are greater when ISVs have greater intellectual property rights or stronger downstream capabilities. The theoretical contribution lie in implying strong IPRs directly mitigate the negative impact of technology commercialization by ISVs. by affecting the likelihood of platform owner entry. In other words, IPRs appear to favor both value appropriation and value cocreation in the enterprise software industry
Background information “The Impact of Information Systems on Organizations and Markets”
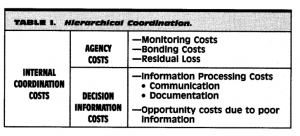
This article examines the impact of information technology on two attributes of firms–firm size and the allocation of decision rights among the various actors in a firm.
The conclusion is 1) a firm may use information systems to decentralize some decision rights and to centralize others, exploiting the merits of both systems and leading to a hybrid structure. 2) when IT plays a significant role in reducing internal coordination costs, a firm may find it advantageous to grow horizontally and vertically. A firm’s use of IT can result in an increase or decrease in either the horizontal or vertical dimension of firm size.
Week 3 Ray et al Yiran
Extant data contradict previous research that the level of vertical integration (VI) has increased rather than decrease with the increasing use of information technology (IT). To address this gap, this paper studies the moderating impact of two measures of competitive environment, demand uncertainty, and industry concentration, on the relationship between IT and VI.
The authors adopt firm level IT spending data from 1995 to 1997 drawn from InformationWeek 500 that had been used in prior research. Matching them with data from other sources, a 2-euation model is used for this paper to address endogenous issue between VI and IT. The results of their analysis show that when demand uncertainty is high or industry concentration is low, IT is associated with a decrease in VI. I. The reason is that IT provides the agility to coordinate with different external partners and specialists. While when in concentrated and in more predictable demand environments, IT may be associated with an increase in VI as firms use IT to coordinate more activities inside the firm to increase revenue, and capture value-add and margin.
This article contribute to the literature by showing the difference in the use of IT across different competitive environments. The implication of this research is that the level of VI may be chosen strategically, given the nature of the competitive environment, which also entails the need for further analysis. Also, since coordination efficiency and effectiveness is possible to affect production costs, future research must explore in greater detail how technology driven coordination and production activities interact, and the implications of this interaction for the level of VI.
Advanced IT in Logistics industry
Integrated TMS Platform
http://markets.on.nytimes.com/research/stocks/news/press_release.asp?docTag=201601110900PRIMZONEFULLFEED6118312&feedID=600&press_symbol=28288804
The Industrial IoT
http://www.forbes.com/sites/stevebanker/2016/01/11/robots-in-the-warehouse-its-not-just-amazon/#2715e4857a0b6b38ed142f80
Robot
http://www.mbtmag.com/article/2016/01/industrial-iot-manufacturing-and-supply-chain-visibility-better
Rai et al.2012 – Yiran
This paper examine the relationship between interfirm IT capability, interfirm communications and relational value. Interfirm communications is defined as the exchange of knowledge, ideas, and opinions driven by goals among senior executives in the interfirm relationships. In this study, the interfirm communications for business development and IT development are measured by total number of visits and phone calls in past year between the supplier’s account executives with the buyers on each aspect. Building on the marketing literature, relational value is operationalized as share of wallet and loyalty.
To conduct the empirical study, they use the active relationships between a Fortune 100 logistics supplier and its buyers in the United States. The findings reveal that IT functionalities, when implemented and used in combination with other resources in the interfirm logistics process (e.g., physical goods, information, and finances across locations), increase relational value. Moreover, higher sophistication of interfirm IT capability profiles would leads to higher relational value. The study also finds interfirm communications for business development can only create relational value with the facilitation of IT capability profiles, whereas interfirm communication for IT development is not found to be contingent on IT capability profiles. As a result, interfirm IT capability profiles have a more substantial role in relational value when relying on interfirm communications for business development.
The contributions of this study include that it theorizes interfirm IT capability profiles as the implementation and use of a set of IT functionalities that combine with other resources to execute interfirm business processes and as a major means for cocreating relational value. Second, this study stresses the importance of the level of sophistication in implicating the IT capability profiles. The sophisticated IT capability profiles accompanied by interfirm communications for business development can significantly enhance the relationship value.