Jeta Gjana
Become Splunk Certified
Hey guys,
Some of you might already know this but for those who have not been notified yet, you can attend 4 online courses and become Splunk certified for free 🙂
Check it out!
http://www.internet2.edu/blogs/detail/10079
Week 13: In the news
“Ransomware, hospital hacking present growing cybersecurity threats”
Hackers crippled computer systems at a major hospital chain, MedStar Health Inc., one of the the largest health care providers in the Baltimore-Washington metropolitan area, on Monday April 1, 2016. Employees were prompted with a note when they tried to open files on their computers requesting payment in bitcoins to unlock the data while forcing records system offline for thousands of patients and doctors. A similar ransomware attack on Hollywood Presbyterian Medical Center in Los Angeles last month led to the hospital paying about $17,000 in bitcoins to regain access to its computer systems. But most importantly, the true risk exists when the hackers can sell the medical record data, alter patient data, access billing information, or manipulate vulnerable devices.
Click here to read more information regarding the above article.
Week 12 Takeaways
Assigned Reading:
Aircrack-ng Suite should be used in a Linux environment and not in a Windows OS since there is not much support for it. For someone who has not been previously exposed to this tool, the simplest process is as follows: determining the chipset in the wireless card, determining which of the three options can be used to run the aircrack-ng suite, and getting starting to use this tool. It is important to properly determine the wireless card chipsets since it needs to be compatible with the aircrack-ng suite. Once that first step is complete, then the user can choose the best option to run that suite. There are three various methods that can run this tool, such as in Linux, a live CD, or a VMWare image.
Question for the class:
What are your experiences thus far running the aircrack-ng suite? What is your preferred method to run it and why?
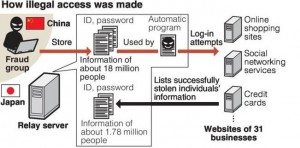
In the news: “18 million stolen IDs discovered on server/criminals in China got illegal access”
The IDs and passwords of about 18 million Internet users have been found on computer server set up by a company named Nicchu Shinsei Corp. in Toshima Ward, Tokyo. The police alleged that the company had provided its customers in China with other people’s IDs to allow them illegal Internet access. The company’s president and other staff were arrested and indicted. The victims were users of major Internet search engine Yahoo Japan, online shopping giant Rakuten, Twitter, Facebook, credit card company Mitsubishi UFJ NICOS Co. and others. It is important to note that the illegal access were conducted from June to November 2015 and the Nicchu Shinsei’s server was used to illegally send money via the Internet banking systems of more than 10 financial institutions.
For more information on the above article, please click here.
Week 11 Takeaways
Assigned Readings:
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.11 is a set of media access control and physical layer for providing connectivity between wireless technology and wired networking infrastructures (i.e.: 900 MHz and 2.4, 3.6.5, and 60 GHz frequency bands). The proper implementation of 802.11 protocol and associated technologies, enables the mobile user to travel to various places (i.e.: lobbies, conference rooms, etc.) and still have access to the networked data. The 802.11 logical architecture is composed of a station (STA), wireless access point (AP), independent basic service set (IBSS), basic service set (BSS), distribution system (DS), and extended service set (ESS). The operating modes include infrastructure mode and ad hoc mode. In the infrastructure mod there is at least one wireless AP and one wireless client whereas in the ad hoc mode, wireless clients communicate directly with each other without the use of a wireless AP. Securing the 802.11 can be challenging but it has certainly evolved over the years using various encryption standards where flaws are still present and can allow a remote attack, such as when a remote attacker recovers the WPS PIN.
In the news:
“Seagate Employee Tax Forms Stole in Phishing Attack”
The W-2 tax documents of several thousand current and former employees of data storage company Seagate ended up in the hands of fraudsters after an employee fell victim to a phishing attack. It is predicted that less than 10,000 employee’s information ended up in the wrong hands. In the meantime, Seagate will cover the costs of a two-year Experian ProtectMyID membership for affected employees. It’s not uncommon for such information to be abused by fraudsters. The tax agency reported last month that cybercrooks had used stolen SSNs to generate over 100,000 PINs on the IRS’s Electronic Filing PIN application. Business email compromise (BEC) scams, such as the one targeted at Seagate, are also increasingly common. Aircraft parts manufacturer FACC AG revealed in January that cybercriminals managed to steal $54 million in a scheme targeting the company’s finance department.
Click here for more information about the above article.
Week 10 in the news
“Hacker’s Typo Tipped Off Authorities on Billion-Dollar Heist”
A spelling mistake in an online bank transfer instruction helped prevent a nearly $1 billion heist last month involving the Bangladesh central bank and the New York Federal Reserve. Unknown hackers still managed to get away with about $80 million. The hackers breached Bangladesh Bank’s systems and stole its credentials for payment transfers. They then bombarded the Federal Reserve Bank of New York with nearly three dozen requests to move money from the Bangladesh Bank’s account there to entities in the Philippines and Sri Lanka. Hackers misspelled “foundation” in the NGO’s name as “fandation”, prompting a routing bank, to seek clarification from the Bangladesh central bank.
For more information, please access the above article here.
Week 8
Since there’s no assigned readings (according to the syllabus), I thought I would share this interesting article: “Office puts chips under staff’s skin”.
Epicenter, a new hi-tech office block in Sweden, are trying a new approach on how they conduct business. The company is implementing an RFID chip about the size of grain of rice under employee’s hand. This allows the 700 employees to access doors, photocopiers, pay in the café all with a touch of a hand.
Even though this is a great idea to allow the convenience of the employee, but what about the actual radio frequency of that chip? How easy is to re-direct the frequency towards that chip or to interfere with other frequencies? It looks like chips will soon replace wearable technology, but how safe and secure are they? I will leave that to future studies…to be continued.
For more information, feel free to access it here.
Week 7 Takeaways
Assigned readings:
Burp Suite is a tool that allows security testing of Web applications. This framework is very powerful for if it is used properly, it identifies vulnerabilities and exploits them. This tool is composed of proxy, spider, intruder, repeater, sequencer, decoder and comparer. Burp intruder allows you to customize attacks against any Web applications and it is composed of four elements: target, positions, payloads and options. SQL Injection testing is also another method that is used within the Burp intruder. Burp repeater manually modifies the HTTP requests and tests the responses given by the page. Burp sequencer checks for the extent of randomness in the session tokens generated by the Web application. Burp decoder sends a request to the decoder and lastly, burp comparer compares between two sets of data. Web application vulnerabilities is becoming more sophisticated however they are various methods to prevent such threats and protect the assets of the company. One of the most common methods include web application scanners and firewalls. Also, it is important to note that managers play a significant role when it comes to web application security.
Question for the class:
What are you experiences thus far using Burp Suite?
In the news: “Vulnerability found in two-factor authentication”
Two-factor authentication is a computer security measure used by major online service providers to protect the identify of users in the event of a password loss. Security experts have long endorsed two-factor authentication as an effective safeguard against password attacks. But what if two-factor authentication could be cracked not by computer engineering but by social engineering? A study was conducted with a scenario in which a hacker, armed only with the target’s mobile phone number, attempts to log into a user’s account and claims to forget the password, triggering a verification SMS text. I n a pilot test of twenty mobile phone users, 25 percent forwarded the verification code to an attacker upon request while proving the success of Verification Code Forwarding Attack.
Click here to read more about this article.
Week 5 in the news
“Keybase Releases Encrypted File-Sharin iPhone App”
Keybase last week announced the alpha release of the Keybase app for the iPhone with a cryptographically secure file mount. Users can write data in an automatically created folder in this format: /keybase/public/username. Files written in the folder are signed automatically and appear as plain text files. The folder prevents server-side and man-in-the-middle attacks. Files stream in on demand; there is no syncing as there is in Dropbox, Google Drive and Box.
For more information regarding this article, please click here.
Week 4 Takeaways
Assigned readings:
Metasploit extended usage includes various capabilities, such as Mimikatz, a user friendly metepreter script composed of various tasks that attackers will want to perform on the initial exploitation phase. There are also various capabilities such as PHP Meterpreter, backdooring exe files, karametasploit, and payloads through MSSQL. Another area that Metasploit unleashed allows is MSF community edition and Armitage. The MSF community edition and Armitage allow scanning, exploitation, and post exploitation.
In the news:
“New Smart Gun Technology Uses Fingerprint Recognition to Childproof Firearms”
The Identilock is a trigger lock device that uses fingerprint recognition to childproof a firearm that starts at $319. It is roughly the size of a man’s palm and fits over the trigger of pistols. It recognizes up to nine different fingerprints, from either different fingers or people, on a square window about twice the size of the biometric sensor on most smartphones. Smart gun technology has been around in some form or another since the late 1990s. Models use fingerprint recognition or a transmitter device within a watch, bracelet or ring to unlock the trigger mechanisms in a gun. The Identilock also comes with a key as a failsafe. And the battery on the lock lasts for 180 days on one charge.
Click here to read more about this article.
Week 3 Takeaways
Assigned readings:
Metasploit Unleashed allows various functions, such as the abilities to conduct MSF Post Exploitation,
Meterpreter Scripting, and Maintaining Access. MSF Post Exploitation allows the user to run privilege escalation, event log management, packet sniffing, pivoting, screen capture, searching for content, etc. For instance, Metasploit uses a script that allows the usage of different techniques to gain access of the System level privileges on the remote system. Meyerpreter Scripting allows the user to look for existing scripts as well as write custom scripts. Lastly, Maintaining Access is composed of keylogging, meterpreter backdoor, and persistent backdoor. Being able to maintain access is key to further examine the target network. Once access is gained into the system, allows you to pivot from one system to another, gain information about the users’ activities by monitoring keystrokes, impersonating users with captured tokens, etc.
Question for the class:
Have you ran any scripts as described in the above techniques before and if so, how successful were you gaining useful information?
In the news:
“Ukraine Mounts Investigation of Kiev Airport Cyberattack”
The cyberattack was related to the BlackEnergy malware attacks that recently targeted Ukranian infrastructure facilities which impacted more than 80,000 customers. This new attack involved a spearphishing email, decoy document, or both, and it was conducted by the Sandworm Team (a team that has been targeting various worldwide entities, such as NATO, EU, etc). Attacking the Kiev Airport was determined by the C2 servers which originated in Russia and disrupting air traffic control system.
For additional information regarding this article, please click here.